How Robotics in Healthcare are Changing Our Future
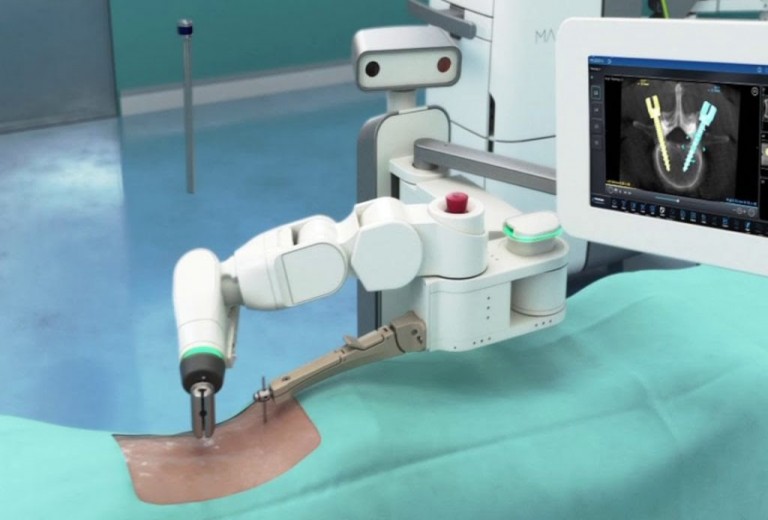
The Impact of Robotics in the Healthcare Industry
Robotics being used in healthcare can be defined as the application and use of robotic technology to diagnose, treat, correct, restore, or modify a body function, body part, or disease.
However, there are many other ways we can see robotics in healthcare used for daily operations. In the healthcare sector, robotics can play a role in sanitization, triage, and even performing actual surgeries; but there is a lot of space in between in which robots in this industry do not meet the standard definition listed above.
The Evolution of Robotics in Healthcare
More often than not, science fiction brings about real innovation and creation.
Robots were once imagined as something so far outside of human control that they could never truly exist. While robotics in healthcare may not be running around looking like C3PO dressed as a nurse or doctor, they have been around for a while.
Starting in the 1980s, robots made an entrance into hospitals with what appeared to be something ripped out of a car production plant and placed into a surgical room to assist in brain biopsies. As technology has evolved, so have these AI-driven assistants.
Robotic arms can be manipulated by a surgeon from a different location to do intricate and delicate surgeries - creating a more sanitary space for both the patient and the surgeon. Robots have also staff handling or carrying hazardous materials and substances, increasing safety in the workplace. They even have the ability to step in and perform routine tasks that might otherwise take nurses and doctors away from patients who need critical human attention.
We may still be years and decades away from having robot nurses or doctors, but there is no question about their usefulness and the eventual necessity of healthcare robots to be taken more seriously.
The Many Functions of Robotics in Healthcare
While we tend to think of the term "robotics" with anthropomorphized mechanical beings in mind, this can be sometimes far from the truth.
Robots in the healthcare industry can take all kinds of forms, shapes, and functions.
One example, is a robot programmed to disinfect a room once a patient has been checked out using ultraviolet light before nurses or other staff arrive to reset the room.
Another example are robotic assistants that can monitor patient vitals while nurses attend to other patients, signaling when there is a need for a human presence in a room. This helps eliminate a potential disaster of something happening to a patient between rounds while nurses struggle to attend to all their patients.
A third example is another form of monitoring robots that can automatically enter patient information into their electronic health record, keeping all attending nurses and doctors up to date on patients in real-time.
Even carts and carriers can be equipped with robotics to transport dangerous or hazardous materials around without the need for human staff to put themselves at risk, similar to the technology used in self-driving cars but on a much smaller and simpler scale.
Advancing Technology for Robotics in Healthcare
As robotic technology continues to evolve, significant advances are being made in the healthcare industry as well.
Robots have been put to use in laboratories that can take samples from patients and transport, analyze, or store them.
This means there is technology being created and perfected for robotics that can detect the best blood vessel in someone's arm to draw blood from and hit it with near-perfect precision, no matter how difficult injecting a syringe may be.
There are robots that can immediately analyze samples – significantly speeding up the process to help patients get information and for medical professionals to make quick and safe decisions.
There are also robots preparing and dispensing medications in pharmacological labs, and they can also interact with pharmacies and submit or edit prescriptions for patients in real time. What used to take hours and sometimes days now can take just a few moments.
Robots for Patient Care
Once a patient has gone through medical treatment at a hospital, robots can be used to help patients through the recovery process. Certain robots are also equipped with special systems to help those who are unable to move on their own – helping patients get their mobility back. In some cases, a robot can even administer physical therapy efficiently without the need for human interaction.
Robots may be some ways away from looking like humanoids, but there are some researchers and engineers creating robots who look and feel more friendly for human users. Different robots have different uses, and not all will need to have a humanized look, but there are plenty of applications where a friendlier face will provide better recovery and put people more at ease as they get the help they need.
For example, Japan is working on technology to improve how human these robots can seem by programming them to understand and even respond to human speech. They can look and feel like they have human skin and tissue, and respond to certain social and emotional cues to make patients feel safe and secure.
Another great use case for robotics in healthcare is for training. If a robot assistant could be created that looks human, feels human, and is programmed to react appropriately to outside stimuli you’ll have a whole new way of potentially helping people more efficiently. Just imagine a robotic emergency assistant responding to patient actions (such as screaming in pain when appropriate, gasping, convulsing, responding well to appropriate treatments, etc.) and then simultaneously offering help, feedback and instruction to the patient.
Are Robotics in Healthcare Threatening Our Jobs?
Will more robots in healthcare destroy jobs? The simple answer is, no. The more complicated answer is, not yet. This is an important question address, because what would we be sacrificing for all of these technological improvements? Would it ultimately help people or harm them?
The most important factor when considering using robots in healthcare is that they can reduce costs in the long-term, but are expensive to purchase and put to use in the short-term (not to mention the development cost by companies bringing them to market).
The average number of hospital beds available per hospital nationwide is about 151 beds (according to the numbers presented on the AHA website from a 2019 study). This does not allow for the average hospital to even have accessible funds to begin utilizing robotics based on their current overhead. So budgets and pricing would also need to change with any influx of robots into medical settings.
What does this mean? Bigger hospitals with bigger budgets will be able to add robotic assistants sooner. Current technology is outside the price range of most hospitals let alone most local healthcare facilities in rural areas. And outside of purchasing the equipment, there’s usually software and other implementation costs associated with the purchase - and implementation doesn’t come cheap.
For example, the use of robotic carts to transport hazardous materials requires the installation of sensors throughout the building to guide these carts, or a special type of mapping of the building (similar to a Roomba robot vacuum). These prices often get overshadowed because hiring a human to do the job, while not a safer choice and does put the staff and potentially others at risk, is much more reasonable in terms of cost efficiency and time efficiency. As the technology eventually becomes cheaper (which it will as technological barriers decrease and widespread adoption occurs), it will make more sense to replace humans with robots for specific tasks.
Ultimately, though, robotics in healthcare can never replicate the benefit of basic human contact. There are conflicting viewpoints on what this will do to people who desire physical human contact rather than a robot. Physical human contact, subtle social and emotional cues, and genuine human interaction are vital to the health, wellness, and safety of patients in healthcare. So it will be difficult to find ways for a robot to replicate the care that a human can give. However, the more likely approach is going to be a hybrid model, which is to use robot assistants to prevent human mistakes, and rely on humans for the human contact and physical interaction that’s so important to patients. If it’s done right, it will work very well.